Summary: Multimodal magnetic resonance imaging (mMRI) has been widely used to map the structure and function of the human brain, as well as its behavioral associations. However, to date, a large sample with a long-term longitudinal design and a narrow age-span has been lacking for the assessment of test-retest reliability and reproducibility of brain-behavior correlations, as well as the development of novel causal insights into these correlational findings. Here we describe the SLIM dataset, which includes brain and behavioral data across a long-term retest-duration within three and a half years, mMRI scans provided a set of structural, diffusion and resting-state functional MRI images, along with rich samples of behavioral assessments addressed - demographic, cognitive and emotional information. Together with the Consortium for Reliability and Reproducibility (CoRR), the SLIM is expected to accelerate the reproducible sciences of the human brain by providing an open resource for brain-behavior discovery sciences with big-data approaches.
Authors:
Jiang Qiu,Ph.D, Professor,Director of the Key Laboratory of Cognition and Personality,Ministry of Education; Director of the Brain Imaging Center,Southwest University
Qinglin Zhang, Ph.D, Professor, Director of the Center for Creativity and Brain Training; Key Laboratory of Cognition and Personality,Ministry of Education
Taiyong Bi,Ph.D, Assistant Professor, Faculty of Psychology, Southwest University.
Gongrong Wu, Ph.D, Assistant Professor, Faculty of Psychology, Southwest University.
Dongtao Wei, Ph.D, Faculty of Psychology, Southwest University.
Wenjing Yang, Ph.D, Faculty of Psychology, Southwest University.
This dataset includes:
USAGE AGREEMENT
Creative Commons License: Attribution - Non-Commercial
Funding
This data repository was supported by:
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (31271087; 31470981; 31571137; 31500885)
National Outstanding young people planthe Program for the Top Young Talents by Chongqing, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (SWU1509383,SWU1509451)
Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing (cstc2015jcyjA10106)
Fok Ying Tung Education Foundation (151023)
General Financial Grant from the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2015M572423, 2015M580767)
Special Funds from the Chongqing Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Xm2015037)
Key research for Humanities and social sciences of Ministry of Education(14JJD880009).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to all of graduate students who contributed their time and wisdom to this data repository, including but not limited to Xue Du, Kang cheng Wang, Jiangzhou Sun, Qunling Chen and Wei Liu. We are also thankful for assistance from Michael Milham and David O'Connor (Child Mind Institute) in constructing the webpage.
SLIM Digital Object Identifier (DOI): http://dx.doi.org/10.15387/fcp_indi.retro.slim
Data Release Table
Derivative connectivity matrices (Dosenbach 160, Shen 268) are also available:
Batch Downloading Data from the FCP-INDI S3 Bucket
Data for SLIM are available for download in an Amazon Web Services S3 bucket. These data are currently organized as follows:
- RawDataTars : Raw data compressed with Gzip and separated by subject ID.
- PhenotypicData : Phenotypic data for participants (i.e., age, sex) stored in csv files by timepoint.
- ConnectivityMatrices: Parcellated fMRI data in .mat format.
Each file in the S3 bucket can only be accessed using HTTP (i.e., no ftp or scp ). You can obtain a URL for each desired file and then download it using an HTTP client such as a web browser, wget, or curl. Each file can only be accessed using its literal name- wildcards will not work.
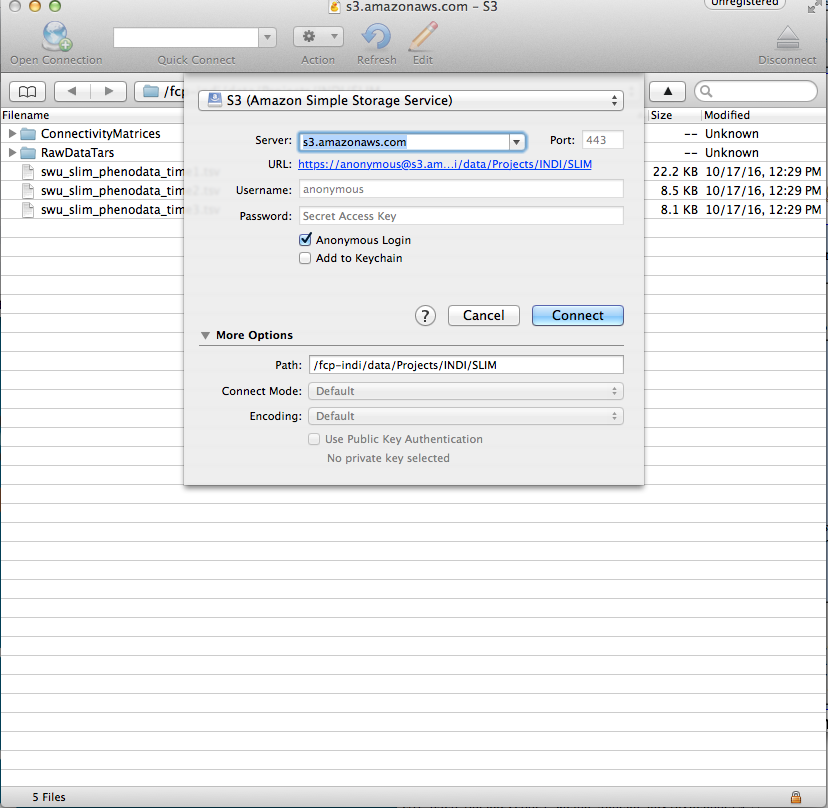
There are file transfer programs that can handle S3 natively and will allow you to navigate through the data using a file browser. Cyberduck is one such program that works with Windows and Mac OS X. Cyberduck also has a command line version that works with Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux. Instructions for using Cyberduck are as follows:
- Open Cyberduck and click on Open Connection.
- Set the application protocol in the dropdown menu to S3 (Amazon Simple Storage Service).
- Set the server to s3.amazonaws.com.
- Check the box labelled Anonymous Login.
- Expand the More Options tab and set Path to fcp-indi/data/Projects/INDI/SLIM/.
- Click Connect.
Once connected it is possible to right-click on a given folder and queue a batch download which will sequentially download all the folders contents.
The end result should appear as follows:
Publications:
Wang, Y., Wei, D., Li, W., & Qiu, J. (2014). Individual differences in brain structure and resting-state functional connectivity associated with type A behavior pattern. Neuroscience, 272, 217-228.
Wang, S., Wei, D., Li, W., Li, H., Wang, K., Xue, S., ... & Qiu, J. (2014). A voxel-based morphometry study of regional gray and white matter correlate of self-disclosure. Social neuroscience, 9(5), 495-503.
Li, W., Li, X., Huang, L., Kong, X., Yang, W., Wei, D., ... & Liu, J. (2015). Brain structure links trait creativity to openness to experience. Social cognitive and affective neuroscience, 10(2), 191-198.
Wei, D., Du, X., Li, W., Chen, Q., Li, H., Hao, X., ... & Qiu, J. (2015). Regional gray matter volume and anxiety-related traits interact to predict somatic complaints in a non-clinical sample. Social cognitive and affective neuroscience, 10(1), 122-128.
Chen, Q., Yang, W., Li, W., Wei, D., Li, H., Lei, Q., ... & Qiu, J. (2014). Association of creative achievement with cognitive flexibility by a combined voxel-based morphometry and resting-state functional connectivity study. NeuroImage, 102, 474-483.
Cun, L., Wang, Y., Zhang, S., Wei, D., & Qiu, J. (2014). The contribution of regional gray/white matter volume in preclinical depression assessed by the Automatic Thoughts Questionnaire: a voxel-based morphometry study. NeuroReport, 25(13), 1030-1037.
Deng, Z., Wei, D., Xue, S., Du, X., Hitchman, G., & Qiu, J. (2014). Regional gray matter density associated with emotional conflict resolution: Evidence from voxel-based morphometry. Neuroscience, 275, 500-507.
Kong, X., Wei, D., Li, W., Cun, L., Xue, S., Zhang, Q., & Qiu, J. (2015). Neuroticism and extraversion mediate the association between loneliness and the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. Experimental brain research, 233(1), 157-164.
Tan, Y., Zhang, Q., Li, W., Wei, D., Qiao, L., Qiu, J., ... & Liu, Y. (2014). The correlation between Emotional Intelligence and gray matter volume in university students. Brain and cognition, 91, 100-107.
Li, H. J., Sun, J. Z., Zhang, Q. L., Wei, D. T., Li, W. F., Jackson, T., ... & Qiu, J. (2014). Neuroanatomical differences between men and women in help-seeking coping strategy. Scientific reports, 4.
Che, X., Zhang, Q., Zhao, J., Wei, D., Li, B., Guo, Y., ... & Liu, Y. (2014). Synchronous activation within the default mode network correlates with perceived social support. Neuropsychologia, 63, 26-33.
Li, H., Li, W., Wei, D., Chen, Q., Jackson, T., Zhang, Q., & Qiu, J. (2014). Examining brain structures associated with perceived stress in a large sample of young adults via voxel-based morphometry. Neuroimage, 92, 1-7.
Sun, J., Li, H., Li, W., Wei, D., Hitchman, G., Zhang, Q., & Qiu, J. (2014). Regional gray matter volume is associated with rejection sensitivity: A voxel-based morphometry study. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 14(3), 1077-1085.
Wei, D., Yang, J., Li, W., Wang, K., Zhang, Q., & Qiu, J. (2014). Increased resting functional connectivity of the medial prefrontal cortex in creativity by means of cognitive stimulation. cortex, 51, 92-102.
Qiao, L., Wei, D. T., Li, W. F., Chen, Q. L., Che, X. W., Li, B. B., ... & Liu, Y. J. (2013). Rumination mediates the relationship between structural variations in ventrolateral prefrontal cortex and sensitivity to negative life events. Neuroscience, 255, 255-264.
Che, X., Wei, D., Li, W., Li, H., Qiao, L., Qiu, J., ... & Liu, Y. (2014). The correlation between gray matter volume and perceived social support: A voxel-based morphometry study. Social neuroscience, 9(2), 152-159.
Yang, W., Liu, P., Wei, D., Li, W., Hitchman, G., Li, X., ... & Zhang, Q. (2014). Females and Males Rely on Different Cortical Regions in Raven\u2019s Matrices Reasoning Capacity: Evidence from a Voxel-Based Morphometry Study. PloS one, 9(3), e93104.
Wang, K., Wei, D., Yang, J., Xie, P., Hao, X., & Qiu, J. (2015). Individual differences in rumination in healthy and depressive samples: association with brain structure, functional connectivity and depression. Psychological medicine, 45(14), 2999-3008.
Yang, W., Cun, L., Du, X., Yang, J., Wang, Y., Wei, D., ... & Qiu, J. (2015). Gender differences in brain structure and resting-state functional connectivity related to narcissistic personality. Scientific reports, 5.
Du, X., Luo, W., Shen, Y., Wei, D., Xie, P., Zhang, J., ... & Qiu, J. (2015). Brain structure associated with automatic thoughts predicted depression symptoms in healthy individuals. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging, 232(3), 257-263.
Li, W., Li, Y., Yang, W., Zhang, Q., Wei, D., Li, W., ... & Qiu, J. (2015). Brain structures and functional connectivity associated with individual differences in Internet tendency in healthy young adults. Neuropsychologia, 70, 134-144.
Chen, Q. L., Xu, T., Yang, W. J., Li, Y. D., Sun, J. Z., Wang, K. C., ... & Qiu, J. (2015). Individual differences in verbal creative thinking are reflected in the precuneus. Neuropsychologia, 75, 441-449.
Yang, J., Tian, X., Wei, D., Liu, H., Zhang, Q., Wang, K., ... & Qiu, J. (2015). Macro and micro structures in the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex contribute to individual differences in self-monitoring. Brain imaging and behavior, 1-9.
Yang, J., Liu, H., Wei, D., Liu, W., Meng, J., Wang, K., ... & Qiu, J. (2015). Regional gray matter volume mediates the relationship between family socioeconomic status and depression-related trait in a young healthy sample. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience, 1-12.
Tong, D., Yang, W., Zhang, Q., Li, W., Wei, D., Che, X., ... & Cao, G. (2015). Association between regional white and gray matter volume and ambiguity tolerance: Evidence from voxel\u2010based morphometry. Psychophysiology, 52(8), 983-989.
Liu, H., Wang, Y., Liu, W., Wei, D., Yang, J., Du, X., ... & Qiu, J. (2016). Neuroanatomical correlates of attitudes toward suicide in a large healthy sample: a voxel-based morphometric analysis. Neuropsychologia, 80, 185-193.
Tian, X., Hou, X., Wang, K., Wei, D., & Qiu, J. (2015). Neuroanatomical correlates of individual differences in social anxiety in a non-clinical population. Social neuroscience, 1-14.
Tian, X., Wei, D., Du, X., Wang, K., Yang, J., Liu, W., ... & Qiu, J. (2016). Assessment of trait anxiety and prediction of changes in state anxiety using functional brain imaging: A test-retest study. NeuroImage, 133, 408-416.
Hao, L., Sang, N., Du, X., Qiu, J., Wei, D., & Chen, X. (2015). Examining brain structures associated with attention networks in a large sample of young adults: a voxel-based morphometry study. Science Bulletin, 60(21), 1824-1832.
Zhu, W., Chen, Q., Tang, C., Cao, G., Hou, Y., & Qiu, J. (2016). Brain structure links everyday creativity to creative achievement. Brain and cognition, 103, 70-76.